“From the beginning he had responded to the avant-garde developments of his time with admirable swiftness and sureness. It is hard to think of another American artist who was receptive to so many different art movements or who managed to win the admiration of everyone from the Surrealists in the 1940s to the Abstract Expressionists in the 1950s to the Pop Artists in the 1960s. Artists who agreed on little else agreed on Cornell.”
—Deborah Solomon
“The central themes of Pop Art were sub-culture, folk cultures, media imagery, new technologies, design, the consumer goods and engineering industries, the inter-relationships between these phenomena and their effect on human beings.”
—Tilman Osterwold
Osterwold’s analysis suggests that traditions, fashions, and even avant-gardist achievements could no longer be the norm after Pop Art, which swept away the boundaries of artistic development with its focus on a “consciously perceived and reflected present-day existence.” Having just finished Deborah Solomon’s biography of Joseph Cornell (Utopia Park: The Life and Work of Joseph Cornell), I am struck by how Cornell anticipated Pop Art with his focus on the appropriated elements of mass culture and his various obsessions with celebrities, while at the same time demonstrating an abiding indifference to the cult of personal fame so typically associated with the movement. Walter Hopps stated that Cornell was “Schwitters’ greatest successor.” Cornell was certainly aware of Schwitters, for he was highly cognizant of nearly everything about the onrushing stream of modern art (in contrast to the misconception that he was some sort of urban hermit), but the precise lineage of artistic influence may never be fully known. Perhaps it was Cornell’s connection with Max Ernst that is a key factor. In my opinion, Ernst was not a giant of 20th-century collage, but did have a vital influence on the genesis of Cornell’s art. It is well recognized that Joseph began and ended his unique body of work with the medium of collage. One of the things that astonishes me is how he could be so attuned to the advancing frontier of present-day art (often staying a step or two ahead of it) and, at the same time, carry such a personal dysfunction that derived from the driving intensity of his inner world. Was that the nature of his genius? At any rate, his strange but amazing ability to synthesize powerful emotional and cultural content by inventing (virtually from scratch) a distilled form of assemblage continues to set the standard for almost everything in the mix of media that has followed in its wake. Hardly a day goes by that I don’t observe an artwork that can be traced directly to his seminal vision. But rarely do I see another artist infuse their juxtapositions with a rich symbolism to compare favorably with his complex associations. Most of the art I see with an obvious Cornellian tone owes more to surrealist automatism or atmospheric illustration than to the intricate blend of embedded meaning and refined intuition that characterized his enduring originality.
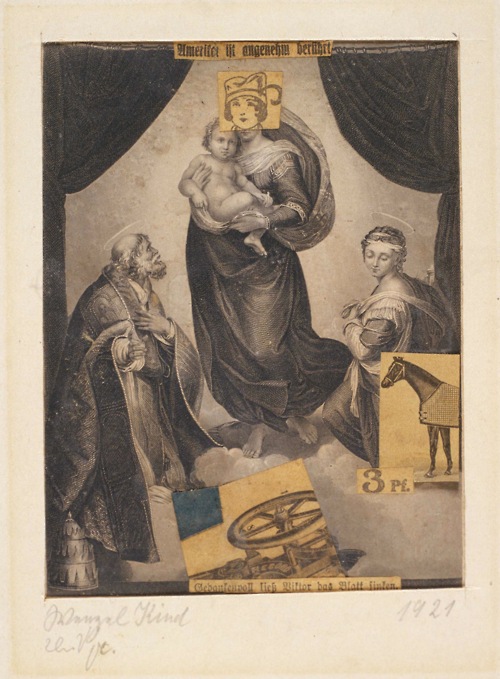

Knave Child
Kurt Schwitters, 1921
Collage on paper
Sprengel Museum, Hannover.
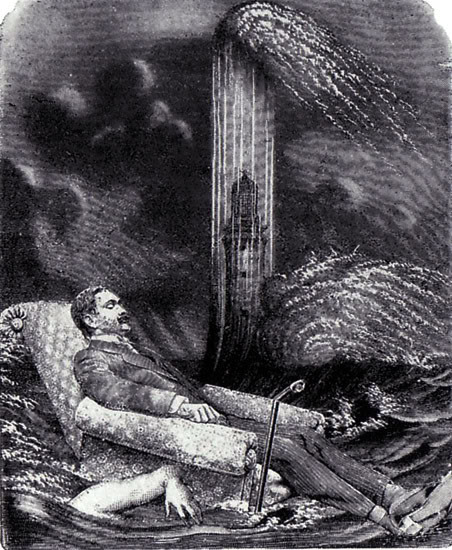

plate from La Femme 100 Têtes
Max Ernst, 1929
Collage novel
Published Éditions du Carrefour, Paris
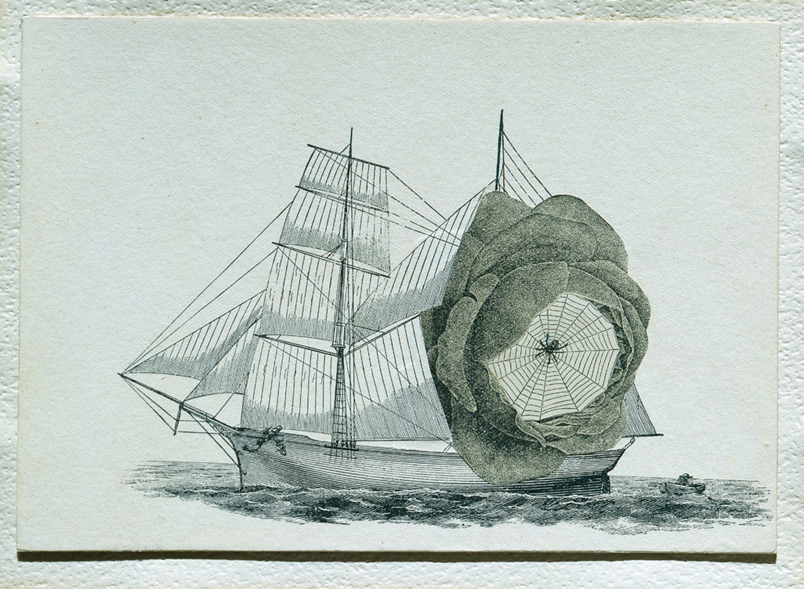

Untitled (Schooner)
Joseph Cornell, 1931
Collage on paperboard

Untitled (Girl and Two Columns)
Joseph Cornell, c. 1950
Glass, wood, tempera and printed paper collage
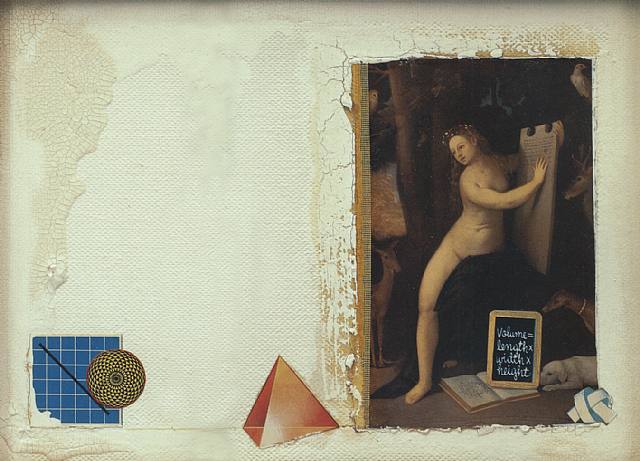

Circe III — Surface and Volume in Nature
Joseph Cornell, c. 1961-66
Collage on masonite